How the Gut Microbiome Works and Why It's Important - An Introduction
Today, we'll delve into the gut microbiome and its significance for overall health.
For good reason, the term "gut microbiome" has been commonly heard about a lot in recent years. The gut microbiome is a collection of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract, and it's becoming clear that these tiny creatures have a significant impact on our health.
But, before we get into the specifics, let's take a step back. The gut microbiome is composed of millions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi that coexist in our intestines. These microorganisms form an ecosystem within our bodies, which has a significant impact on our health. In fact, the gut microbiome is so important that it has been designated our "second brain."
The effects of the gut microbiome on gene expression are one of the most important ways that it affects our health. This is both critical and potentially great news. Genes are the instructions that tell our cells how to behave, and gene expression is how those instructions are carried out. The gut microbiome has been shown to influence gene expression in both positive and negative ways.
For example, studies have shown that the gut microbiome can influence gene expression in the development of obesity and metabolic disorders. According to research, gut microbiome imbalances can alter the expression of genes involved in immune function and inflammation, leading to the development of inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, on the other hand, has been shown to have a positive effect on gene expression. Certain probiotics have been shown in studies to alter the expression of genes involved in detoxification, antioxidant protection, and innate immunity, all of which can help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
In short, the gut microbiome is vital to overall health, and its effects on gene expression are just one of many ways it affects our bodies. We can improve our health and lower our risk of chronic diseases by understanding the gut microbiome and how to maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms.
Yes, the gut microbiome is the community of microorganisms that live in the gastrointestinal tract. This community is made up of a wide variety of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and it plays an important role in the gut's functioning and overall health. The term "probiotic" is derived from the Greek words "pro" (meaning "for") and "bios" (meaning "life"). It was first coined in 1965 by a scientist named Lilly and defined as "organisms and substances that have a beneficial effect on the host by contributing to its intestinal microbial balance."
When we talk about the gut microbiome, we usually mean the bacteria that live there, because they make up the majority of the microorganisms. These bacteria are known as commensal or probiotic bacteria, and they perform a variety of important functions in the body, including:
- Food digestion: Certain types of gut bacteria aid in the breakdown of complex sugars and fibers in our food that we cannot digest. This not only aids in the extraction of more energy and nutrients from our food, but it also produces short-chain fatty acids, which have a variety of health benefits.
- Immune system: The gut microbiome also plays an important role in immune system development and function. The gut microbiome helps to train these cells to distinguish between "good" and "bad" bacteria, which can help to prevent infections and inflammation.
- Mental Health: The gut microbiome has a close relationship with the brain via the gut-brain axis, which is the communication pathway between the gut and the brain. According to research, gut bacteria can influence the brain in a variety of ways, including influencing the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which can affect our mood and mental health.
A variety of factors, including diet, medications, stress, and disease, can alter the composition of the gut microbiome. Dybiosis, or an imbalance in the gut microbiome, can cause a variety of health problems, including digestive disorders, allergies, autoimmune diseases, and more.
What You Eat Makes A Big Difference
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is critical for overall health, and there are several ways to do so, including:
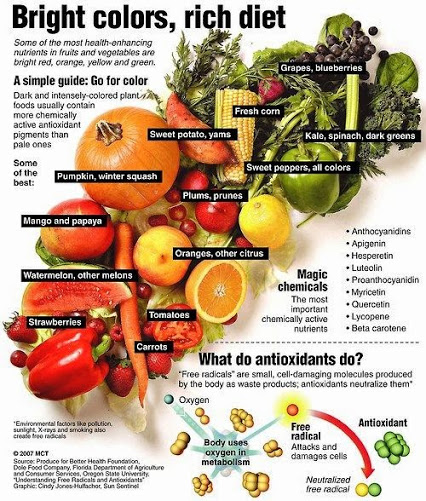
- Consuming fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods: These foods are high in fibers and prebiotics, which are nutrients that gut bacteria require to grow and thrive.
- Avoiding processed foods: Processed foods are frequently high in added sugars and preservatives, which can disrupt the gut microbiome's balance.
- Use antibiotics sparingly: Antibiotics can kill both good and bad bacteria, causing an imbalance in the gut microbiome.
- Taking probiotics: Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir and can help to increase the population of beneficial bacteria in the gut. It is assumed that not all yogurt is created equal, some pack much more sugars than others.
To summarize, the gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of microorganisms that play an important role in health maintenance and disease prevention. A healthy gut microbiome is necessary for proper digestion, immune function, mental health, and overall well-being.
To elaborate on the importance of the gut microbiome, it is important not only for the physiological functions mentioned earlier, such as digestion, immune system, and mental health, but it also has a significant impact on other bodily systems and processes, such as:
- Cardiovascular health: Research has shown that the gut microbiome can influence the development of heart disease by influencing lipid metabolism and inflammation. A disruption in the gut microbiome has been linked to an increased risk of hypertension, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis.
- Skin health: The gut microbiome is important for the immune system of the skin, as well as the production of certain skin lipids that maintain barrier function and protect the skin from environmental stressors. Eczema, psoriasis, and acne can all be caused by a disruption in the gut microbiome.
- Neurological disorders: Although research in this area is still in its early stages, studies have shown that the gut microbiome may play a role in the development of neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. The gut microbiome is thought to influence the development of neurodegenerative diseases via its effects on inflammation, immune function, and the gut-brain axis.
- Cancer: It has been demonstrated that the gut microbiome influences the development and progression of certain types of cancer, such as colon cancer. This is thought to happen due to the effects of the gut microbiome on inflammation, immunity, and gene expression.
It is important to note that the gut microbiome is both an indicator and a modulator of health. When the gut microbiome is in balance, it can aid in disease prevention and health promotion. When the gut microbiome is out of balance, however, it can contribute to the development of a variety of health problems.
As a result, maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is critical for overall health and wellness. This can be accomplished by eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, fermented foods, and probiotics, as well as limiting processed foods and antibiotic use. Furthermore, other lifestyle factors that may affect the gut microbiome, such as stress, physical activity, and sleep, must be considered.
Consultation with healthcare professionals and experts that understand the importance of gut health can aid in determining whether or not there are any imbalances in the gut microbiome, as well as in developing personalized strategies to maintain and improve the gut microbiome for optimal health.