The Gut Microbiome and Digestion
Hello, and welcome back to HealthyRant, where today we'll be delving even further into the fascinating world of the microbiome found in the gut! Today, we will be concentrating on the microbiome of the gastrointestinal tract as well as digesting, which is one of the most important jobs that this miniature ecosystem within our bodies is tasked with doing.
As previously discussed, the microbiome of the gut is made up of millions of different types of microorganisms that dwell in the digestive tract. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, and fungus. But were you aware that these very small organisms play a significant role in the digesting process?
The complex carbohydrates and fibers that are present in our diet but that humans are unable to digest on our own are broken down by gut flora. This not only aids in the extraction of more energy and minerals from the food we eat, but it also results in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which have a variety of positive effects on one's health. For example, SCFAs have the ability to combat inflammation and also serve as a source of energy for the cells that line the colon.
However, this is not the only factor involved; the bacteria that live in the digestive tract are also essential to the process of absorbing nutrients. Certain vitamins, such as vitamins K and B12, as well as other necessary molecules, such as amino acids, can be synthesized with the help of the microbiome that lives in the gut.
The movement of both food and waste through the digestive tract is referred to as gut motility, and it is largely controlled by the bacteria that live in the gut. They play an important role in the fermentation process, which results in the production of gas and can help things move along more smoothly in the digestive tract. Issues with gut motility, such as constipation or diarrhea, might be the result of an imbalance in the microbiota of the intestines.
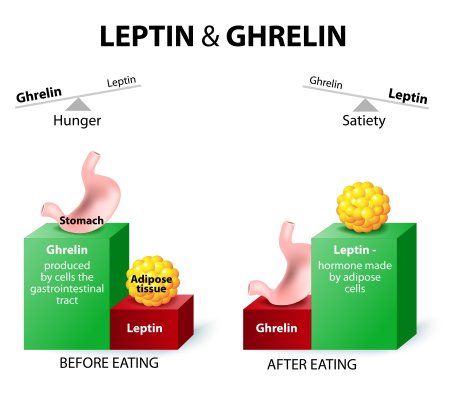
In addition, the microbiome of the stomach plays a significant part in the regulation of both hunger and the feeling of being full. Researchers have discovered that the microbiome of the stomach can have an effect on the release of hormones that govern appetite and fullness, which in turn can have an effect on how effectively one manages their weight.
Now, let's talk about several illnesses of the digestive tract that are directly associated to abnormalities in the gut microbiome.
Irritable bowel syndrome, also known as IBS, is a common digestive ailment that primarily affects the large intestine. This condition has been connected to an imbalance in the microbiota of the gut. According to the findings of several studies, individuals who suffer from irritable bowel syndrome have a distinct bacterial makeup in their intestines compared to healthy individuals.
Another illness of the gastrointestinal tract that has been connected to an imbalance in the microbiome of the gut is inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Research has indicated that patients who suffer from inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, have a different make-up of gut bacteria than healthy individuals do.
The list does not end here; abnormalities in the gut microbiome have been linked to a wide variety of additional gastrointestinal illnesses, including the following:
GERD, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Celiac disease - bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine (also known as SIBO)
- Gastric cancer
It is abundantly obvious that the microbiome of the intestines plays an essential part in digestion, the absorption of nutrients, and the overall health of the intestines. We can take measures to improve our gut health and lower our risk of gut illnesses if we have a better understanding of the gut microbiome and how to maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the gut.
Critical Note: What is so fascinating to me, is that there is a possibility to change gene expression with microbiome manipulation! Recent research has shown the microbiome can interact with our genes, changing their expression and impacting our health in numerous ways.
So, what can we do to ensure that the microbiome in our guts remains in good health?
- Consuming a diet that is abundant in fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods: These foods are rich in fibers and prebiotics, which are the essential nutrients for the development and survival of the bacteria that live in the gut.
- Staying away from processed meals: Processed foods typically have a high amount of added sugars and preservatives, both of which can throw off the delicate microbial balance in the stomach.
- Taking probiotics: Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be found in fermented foods like yogurt and kefir, and they can help to enhance the population of healthy bacteria in the stomach. Probiotics can be taken as a supplement, or they can be found in fermented foods.
- Reducing the amount of antibiotics one takes Antibiotics have been shown to kill out both beneficial and harmful bacteria, which can cause an imbalance in the microbiome of the stomach.
In conclusion, the microbiome of the gut plays an important part in digestion as well as the health of the gut as a whole. We can take measures to improve our gut health and lower our risk of gut illnesses if we have a better understanding of the gut microbiome and how to maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the gut.
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota can be accomplished in a number of ways, including eating a diet that is abundant in fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods; avoiding processed foods; taking probiotics; and using antibiotics only as a last resort. In addition, it is essential to take into account the other aspects of lifestyle, such as stress, physical exercise, and sleep, which have the potential to influence the microbiome found in the gut.
If you are experiencing concerns that are related to your gut or if you suspect that there may be an imbalance in the microbiome of your gut, you should make sure to speak with your healthcare expert and ask for help on how to enhance the health of your gut.